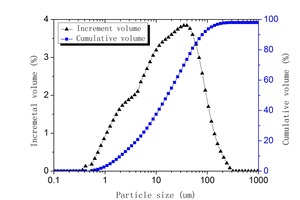
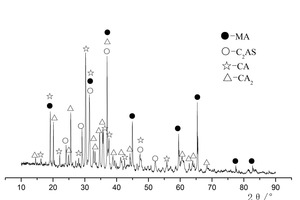
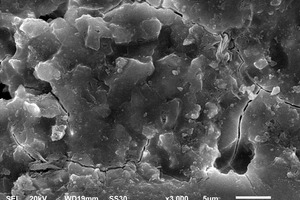
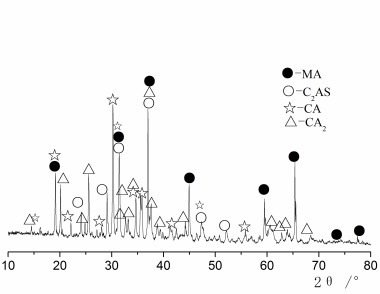
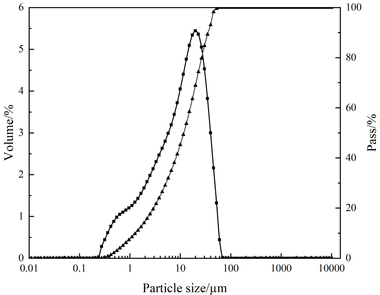
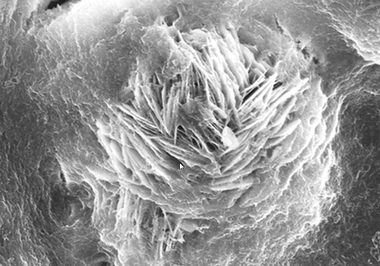
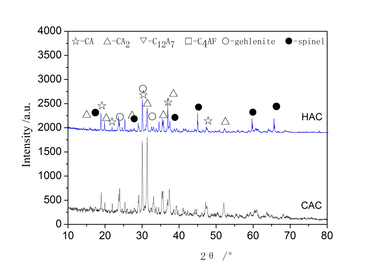
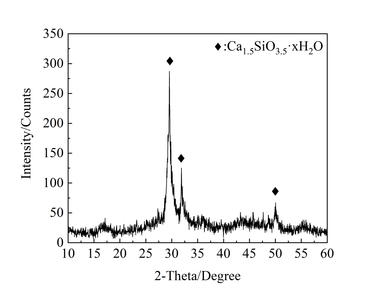
Effect of cupric nitrate on the hydration of remaining slag from titanium-bearing BF slag
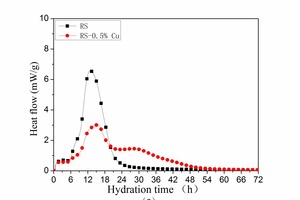
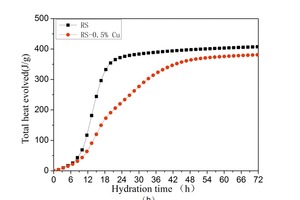
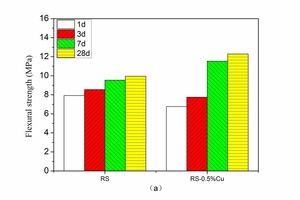
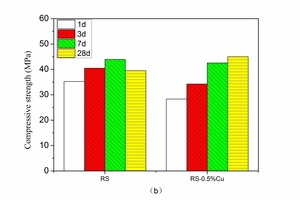
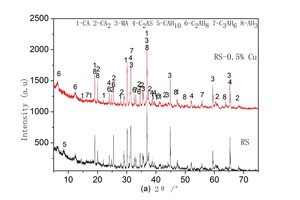
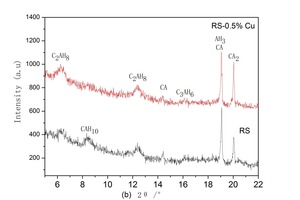
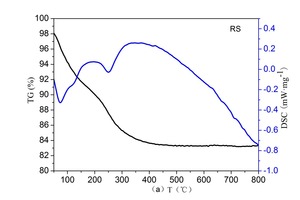
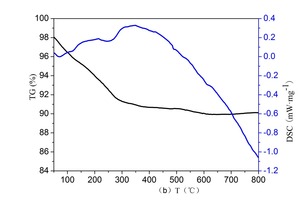
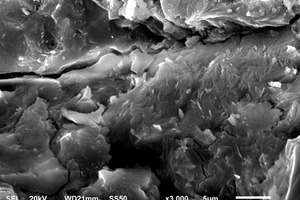
The aim of this work is to investigate the effect of 0.5 % addition of cupric nitrate on the setting time, heat flow curves, hydration and compressive strength of remaining slag (RS) from a Ti-Si-Fe making process based on titanium-bearing BF slag, the chemical and mineral compositions of which are similar to those of calcium aluminate cement. Cupric nitrate can cause a delay in the initial setting and final setting time of remaining slag. Maximum heat liberation occurs later and less pronounced when cupric nitrate is added. Hydration was identified by means of XRD,TG-DSC and SEM. All results showed the hydration products at 1d of CAH10 to have decreased significantly in RS laced with Cu, while the C2AH8 content increased at first, later converting to stable C3AH6 with continuing hydration.
1 Introduction
Heavy metal-bearing waste generally requires solidification/stabilization (S/S) [1-3] which is a processing method of high efficiency, low cost and low risk causing no secondary pollution or exposure. Cu has strong migration, enrichment and hidden, non-biodegradable, easy-to-cause chronic poisoning, carcinogenicity, deformity, mutagenic effect [4]. Cement-based materials such as Portland cement, calcium aluminate cement and calcium sulphate cement are the most adaptable types of binder currently available for S/S [5-9].
Portland cement can reduce the leaching of heavy metals,...