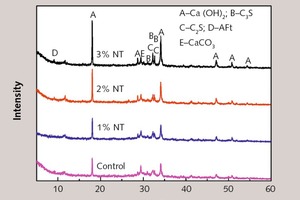
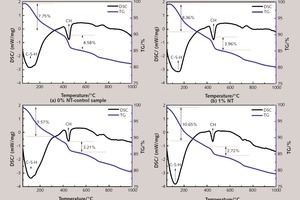
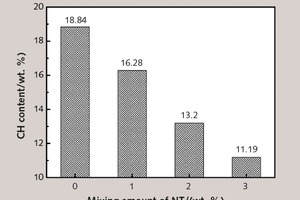
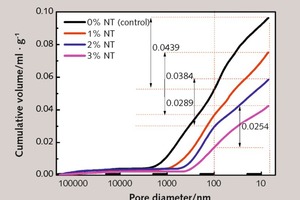
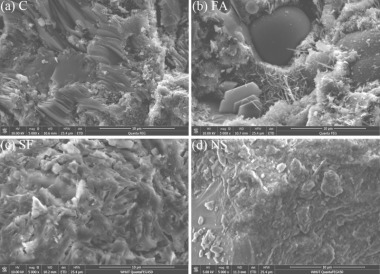
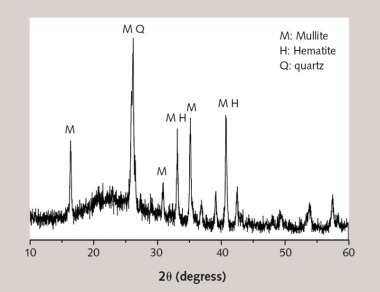
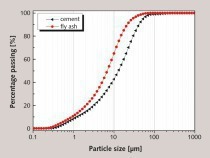
Effect of nano-TiO2 on chloride ingress in cementitious material
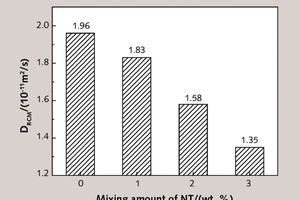
The influence of nano-TiO2 (NT) on impermeability to chloride ions of mortars was studied by the rapid chloride migration (RCM) method, and the improvement mechanism was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry-thermogravimetry (DSC-TG), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP). Results show that the addition of NT helps strengthen the chloride resistance of mortars. Dosages of 1 %, 2 % and 3 % reduce the chloride diffusion coefficient by 6.6 %, 19.4 % and 31.1 %, respectively. It is concluded from mechanism analysis that the micro-aggregate filling effect and the heterogeneous nucleation effect promoting the generation of hydration products of NT, together affect the pore structure and compactness of mortars, further improving their ability to counter chloride diffusion.
1 Introduction
Severe durability problems caused by chloride ingress into concrete in a marine environment, such as reinforcement corrosion, cracking and peeling, performance degradation and decrease of service life, have attracted widespread research attention. External chloride ions migrate into concrete primarily through pores within cementitious materials, so it is obvious that the anti-chloride ion permeability of concrete is closely related to its pore structure. Research by Anders et al. [1] found that the capillary porosity of cement paste increased along with the water-cement ratio....