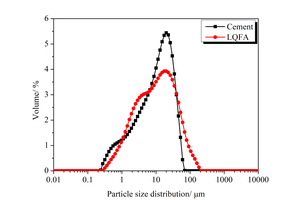
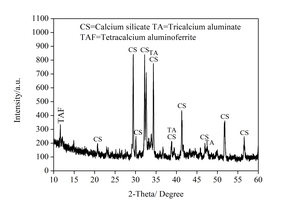
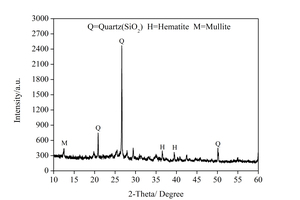
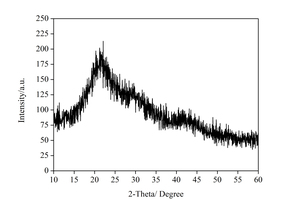
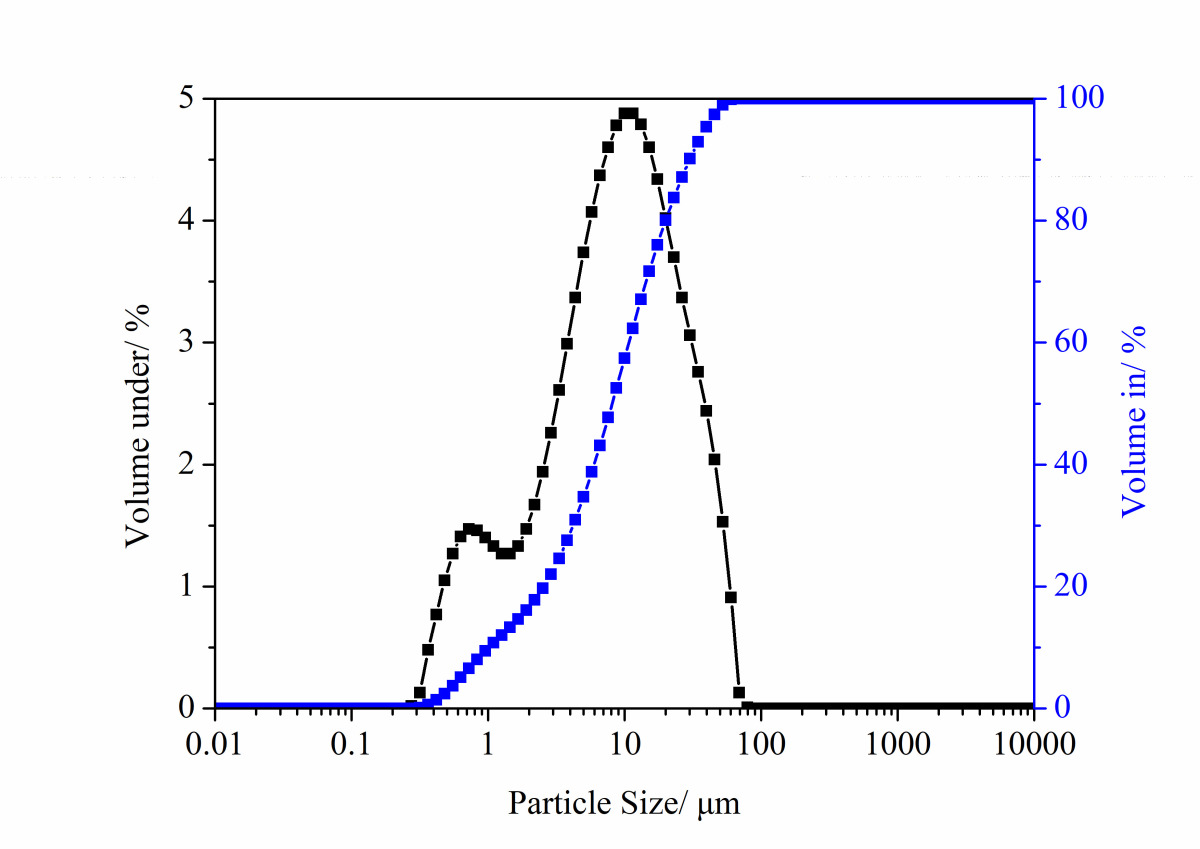
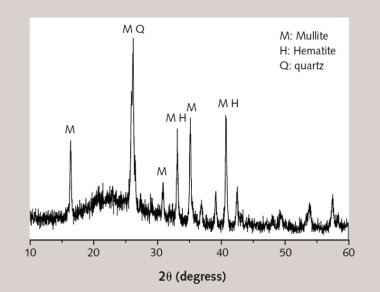
Effect of nano-SiO2 on the strength and hydration characteristic of low quality fly ash-cement system
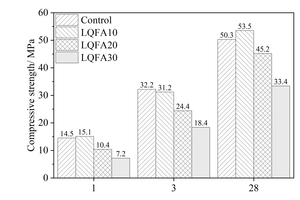
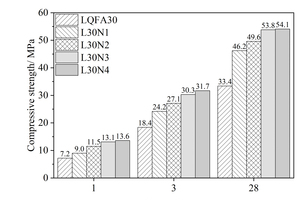
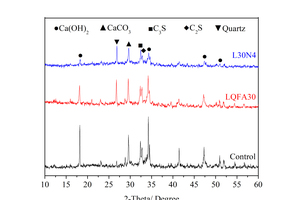
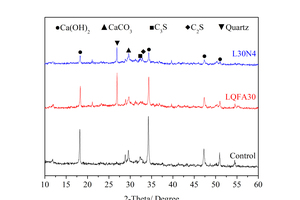
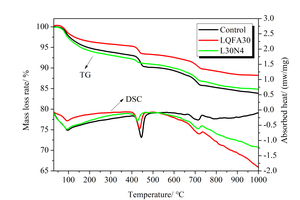
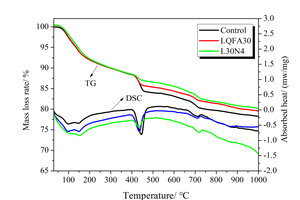
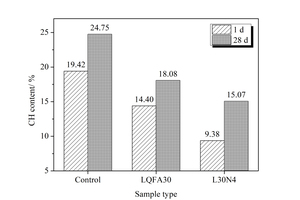
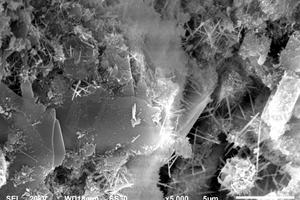
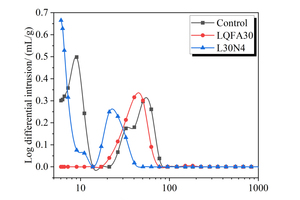
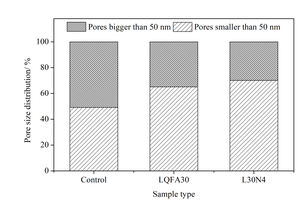
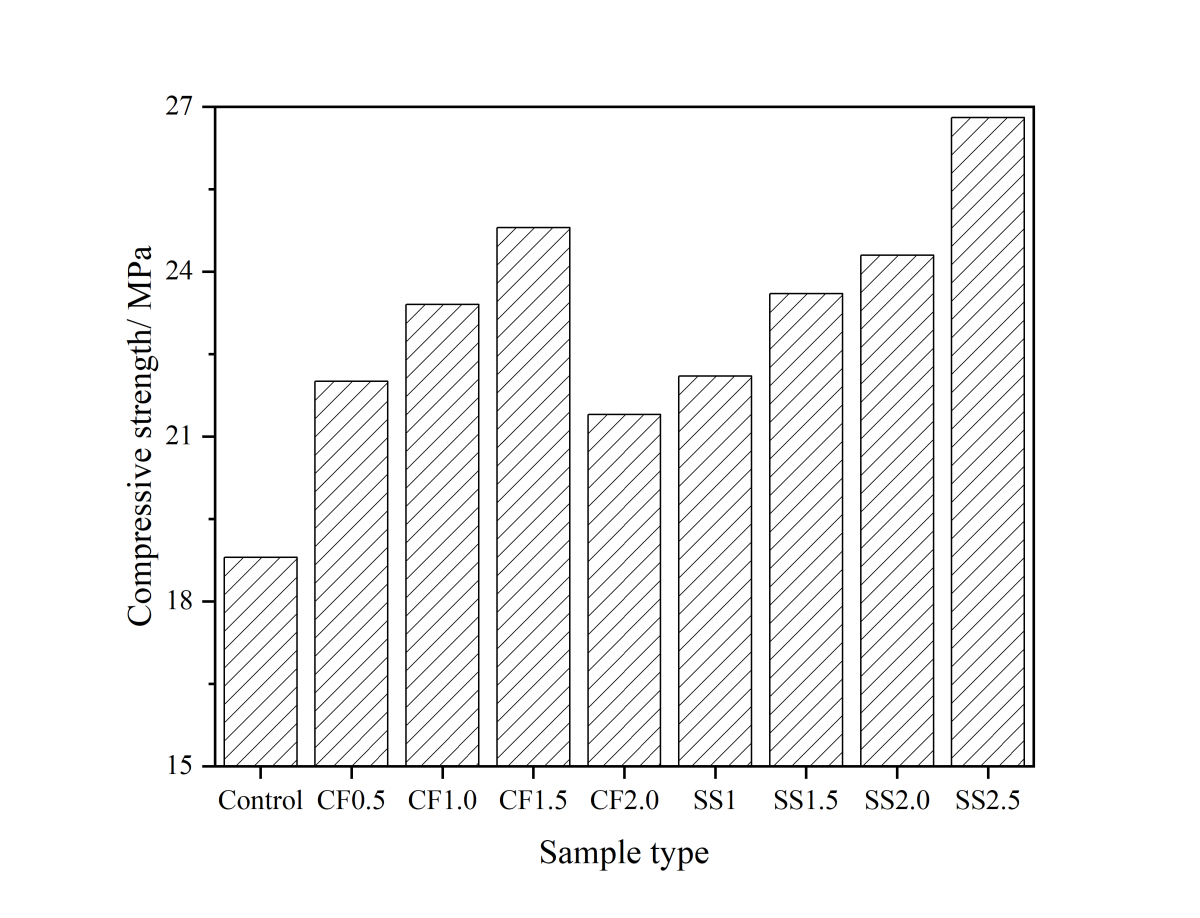
Generally, low quality fly ash (LQFA) is a kind of micron industrial by-product which seriously affects the strength of cement-based materials, and in order to explore a method to improve this disadvantage, the effect of LQFA and nano-SiO2 (NS) on compressive strength were investigated. To reveal the mechanism behind this, the influence of LQFA and NS on hydration characteristics and microstructure of the cement matrix were also studied by XRD, DSC-TG, SEM and MIP. Results show that when the content of LQFA is more than 10%, the early strength of hardened cement paste decreases significantly, and the larger the dosage, the greater the reduction. Further addition of NS can improve the strength drop caused by LQFA incorporation due to its micro-filling effect, crystal nucleus effect and chemical activity. In the hydration process of the LQFA-cement system, NS can not only consume a lot of CH to generate compact C-S-H, but also play a role of filling effect, leading to the improvement of pore structure, an increase in compactness and uniformity, and an enhancement in compressive strength. The results can provide a reference for the application of LQFA and NS in cement-based materials.
1 Introduction
Fly ash (FA) is a micron industrial by-product, which can cause a waste of land resources and environmental pollution when piled up in large quantities. However, its chemical composition is similar to cement, which means that it reacts with cement hydration products to produce a certain gelling property. Therefore, its incorporation into cement can not only adjust the mixing ratio of binding materials and reduce the amount of cement, but also reduce the carbon emission in the production process of cement clinker. In addition, the incorporation of FA into cement can also reduce...