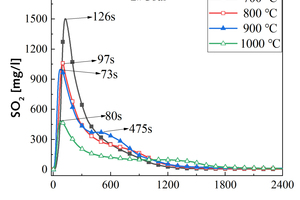
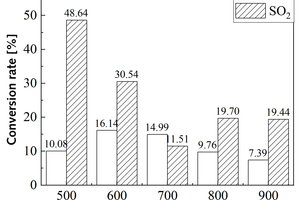
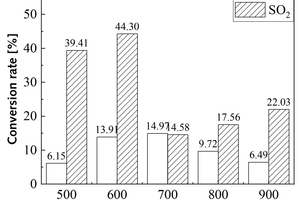
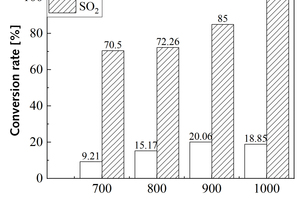
Effect of precalciner collaborative disposal of RDF and bituminous coal on the generation and transformation of NOx and SO2
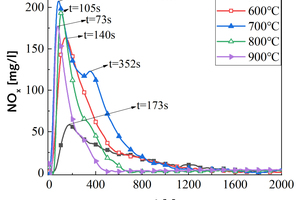
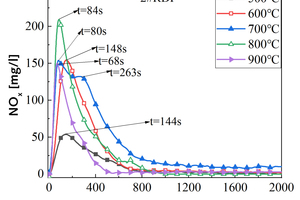
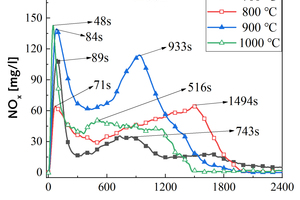
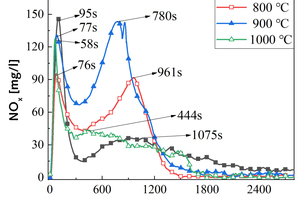
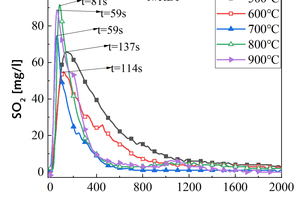
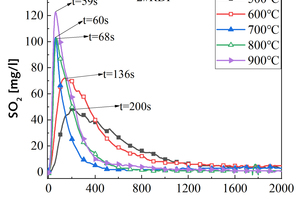
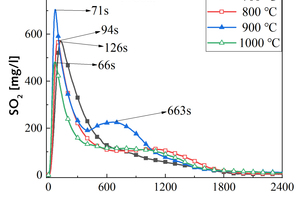
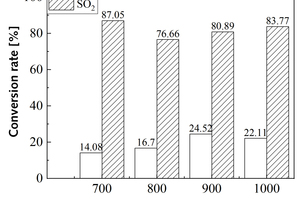
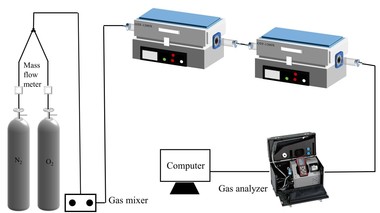
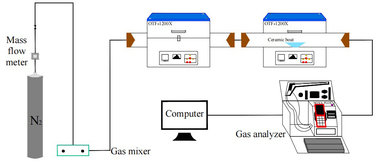
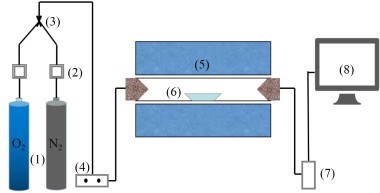
It is one of the current development trends to utilize cement kilns to dispose of refuse derived fuel. However, there is a problem of unstable pollutant discharge in the actual disposal process. This paper takes refuse derived fuel disposed via a cement plant in China and two kinds of standard bituminous coal as the research object and conducts experiments with a high-temperature tubular furnace. The release characteristics of NOx and SO2 from two kinds of refuse derived fuel at 500~900 °C and two kinds of bituminous coal at 700~1000 °C were studied. The experimental results showed that the peak concentration of NOx was more affected by temperature at low temperature (500~600 °C), and the peak concentration of NOx refuse derived fuel was less affected by temperature at high temperature (700~900 °C). In the process of bituminous coal combustion at various temperatures, the first peak value of NOx was less affected by temperature, and the second peak value was more affected by temperature. In the combustion process of two kinds of refuse derived fuel, the conversion rate of NOx showed an “inverted V” shape with the change of combustion temperature, while the conversion rate of SO2 showed a “positive V” shape with the change of combustion temperature. Both NOx and SO2 played a mutually inhibitory role in the formation process. At 1000 °C, the combustion efficiency of bituminous coal was low, and a few drops of substance containing N in bituminous coal would be released with the complete combustion of C, while a large amount of substances containing S in bituminous coal would be released with the complete combustion of C.
1 Introduction
The increasing production of cement has led to a significant increase in coal consumption. Under the typical pulverized coal combustion state, NOx is mainly generated by nitrogen oxidation in coal, accounting for more than 80% [1]. Refuse derived fuel (RDF) has the characteristics of high calorific value, stable combustion, ease of transport, ease of store, low secondary pollution and low emissions of dioxins. The application of RDF as an alternative fuel for coal in the cement industry can not only reduce the production cost of enterprises, but also realize the utilization and...