Status quo of co-incineration of solid recovered fuels in Germany
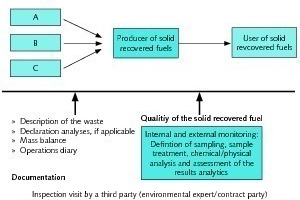
The status quo of co-incineration in Germany and the production of quality assured solid recovered fuels (SRF) is as well described as the normative requirements for the production of SRF, which actually develop to international standards. Finally, the contribution of co-combustion to the climate and resource protection is illustrated.
1 Introduction
In Germany, co-incineration of solid recovered fuels in industrial combustion plants like coal-fired power plants and cement plants is an inherent part of modern closed loop recycling management, because this allows high-class utilization of materials with a high heating value. Thereby, solid recovered fuels are defined as a variety of fractions for energetic use, which are produced from non-hazardous wastes [14].
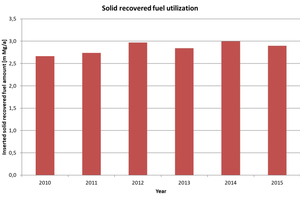
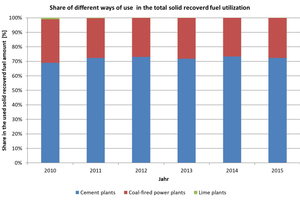
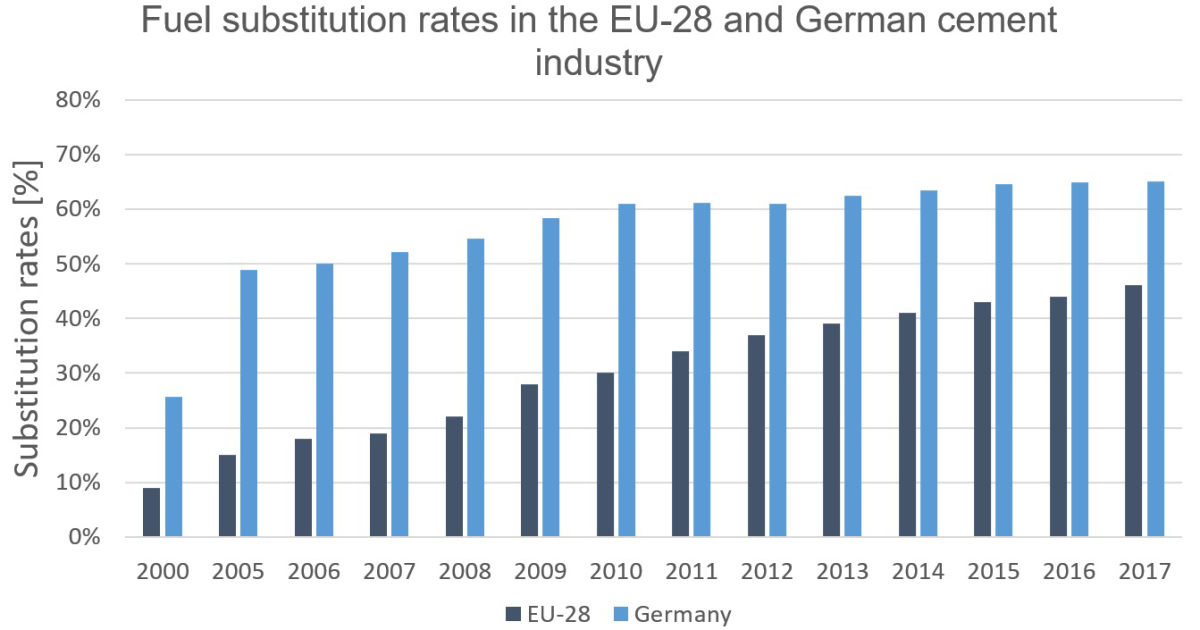
Solid recovered fuels are mainly used in cement, lime and coal-fired power plants. The total amount of solid recovered fuels used in these industries is about 2.75 - 3...