Buttering to be on the safe side – six material technology advantages of buttering
It is generally known that the buttering-floating method promises better adhesion. But why is this actually so? The following article describes six advantages of the combined method and explains the background.
1 Introduction
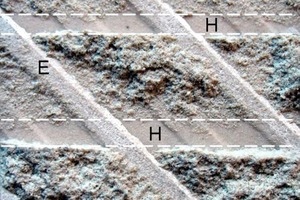
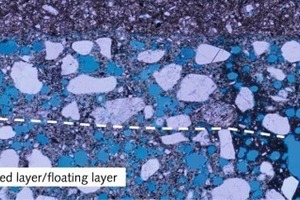
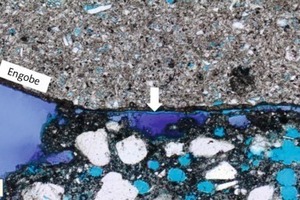
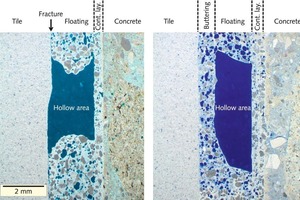
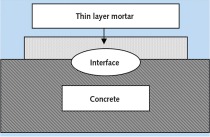
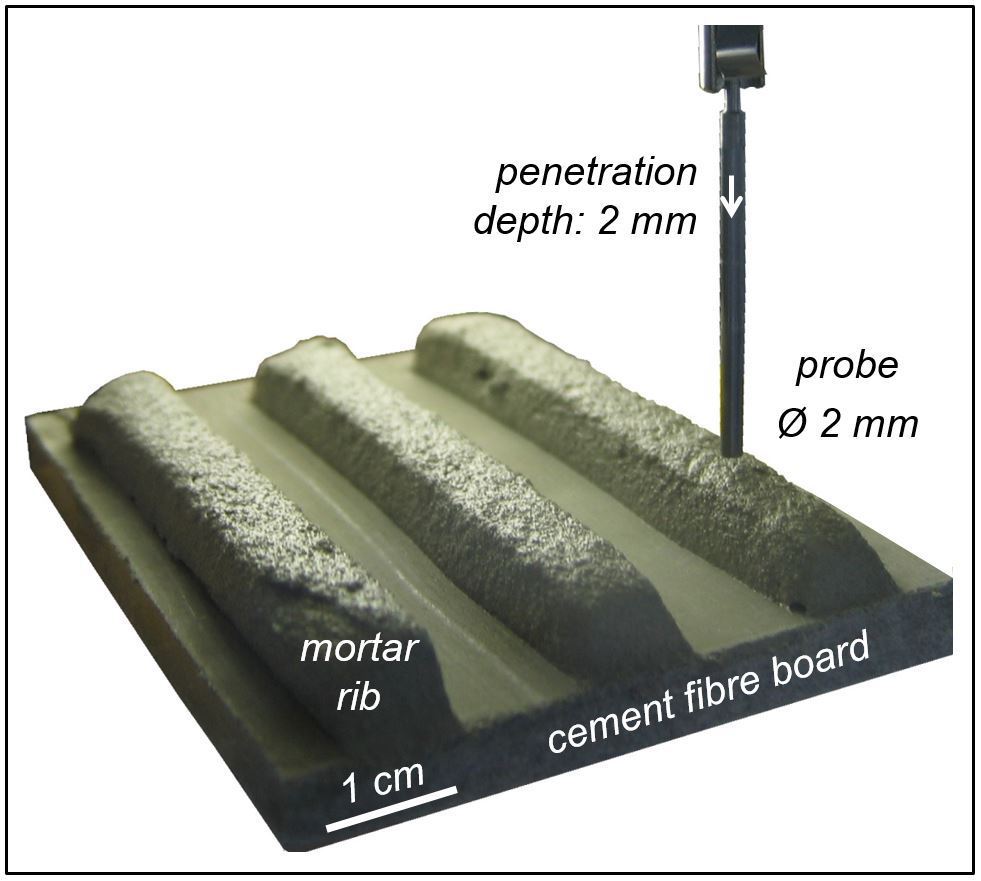
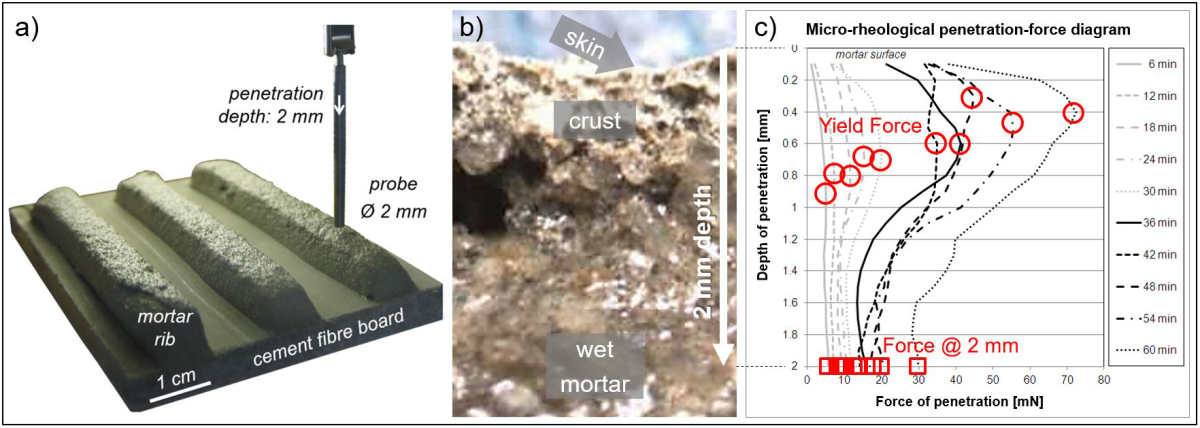
Two very different material surfaces come into contact when a porcelain tile is placed by the floating method. On one side there is the previously combed mortar that forms a thin dry skin with increasing exposure time (time between mortar trowelling and embedding of the tile) and reduces the wettability of the mortar surface. On the other side is the rear side of the tile manufactured in the factory that may be covered with chalky coatings or other forms of dust that can act as separating agents. If these two material surfaces are to form a durable bond then optimum wetting and...