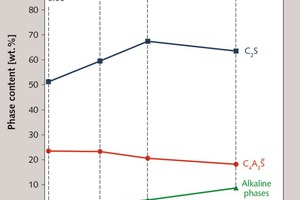
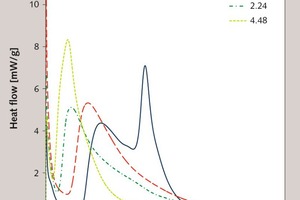
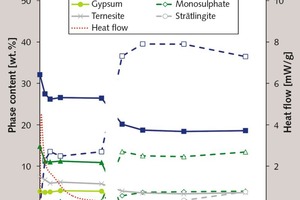
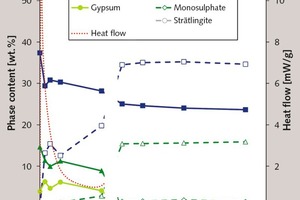
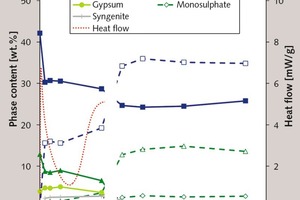
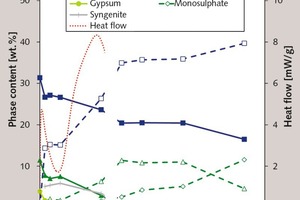
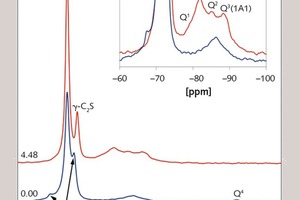
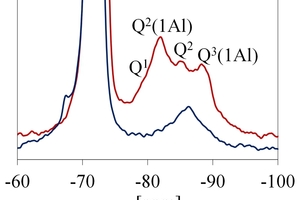
Effect of alkali content of raw meal on composition and hydration of belite‑calcium sulfoaluminate cement
The aim of the present investigation is to design a suitable raw meal which when burnt yields a belite-rich clinker with calcium sulfoaluminates. However, using different fly ashes with different mineralogical and chemical compositions in the raw meal affects the composition of the clinker. This study considers the effect of different alkali contents in a model system based on a raw meal with fly ash on clinker composition and the hydration behaviour. Thus, the effect of using different fly ashes in the raw meal can be estimated in advance. Results are presented for heat flow calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, simultaneous thermal analysis and solid state NMR measurements.
1 Introduction
Currently about 2.8 billion tonnes of cement are produced every year worldwide. An increase in production of up to 4 billion tonnes can be assumed by 2050 [1, 2]. The highest increase is likely to take place in China and India, but also in regions such as the Middle East and North Africa.
In this time of CO2 economies and ecological certification for buildings, Portland cement represents a building material with high consumption of raw materials and high CO2 emission. For specific applications, e.g. self-levelling floor screed, Portland cement can be replaced by low-energy cements...