Effect of mineralogical substitution raw material mixing ratio on mechanical properties of concrete
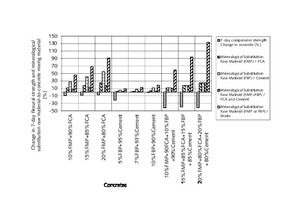
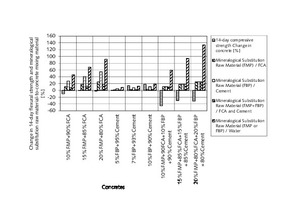
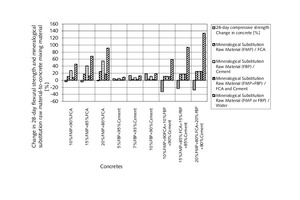
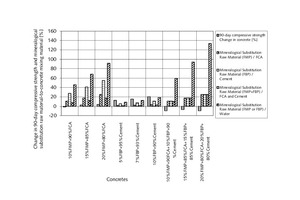
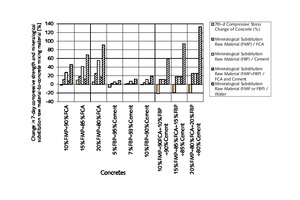
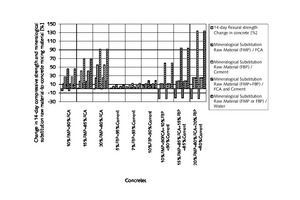
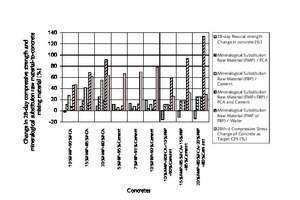
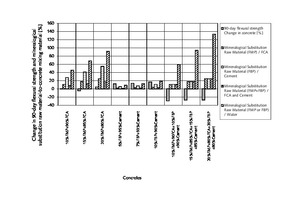
The aim of the original research was to examine and discuss the effects of mineralogical substitution raw material mixing ratios on some mechanical properties of concrete. In this study, fine-particle marble-cutting remnants and fine-particle burnt-clay brick remnants, fine and coarse crushed aggregate, CEM I 42.5N cement and tap water are used as concrete mixing materials. The mineralogical raw substitution material mixing ratio is an independent variable for concrete strength properties. Three substituted concrete groups and one control concrete group were prepared with and without substitution of fine-particle marble-cutting remnants and/or fine-particle burnt-clay brick remnants. The 7-, 14-, 28-, and 90-day compressive strength and flexural strength of concrete were measured with regard to the effects of the mineralogical raw substitution material mixing ratio. The findings unveil that the mineralogical raw substitution material mixing ratio can have positive effects on some mechanical stress factors affecting concrete.
1 Introduction
Turkey has abundant marble reserves and numerous marble-cutting ateliers and factories. Brick is manufactured at about 520 small and medium-sized factories in Turkey. With a total of 57 cement factories, Turkey is a leading producer country in Europe. Indeed, Turkey is one of the top 10 manufacturers in the world [1]. As marble and brick are processed, mineralogical raw material is generated as particulate and scrap material (remnants). According to calculations performed by the author, about 2.592 million t of marble remnant and 3.8 million t of brick remnant accrues in Turkey...