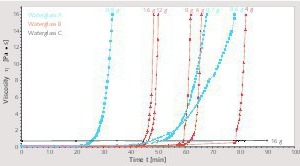
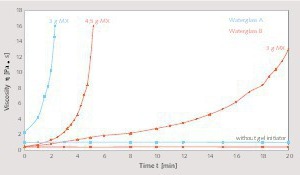
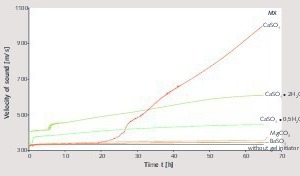
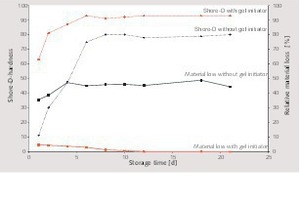
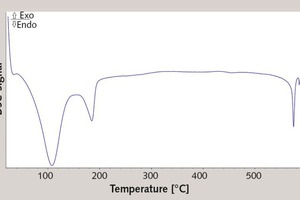
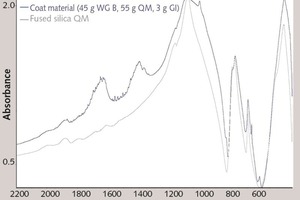
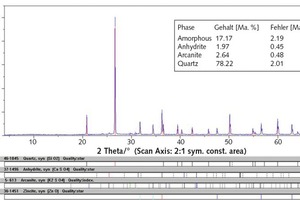
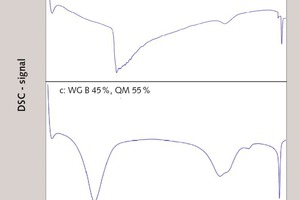
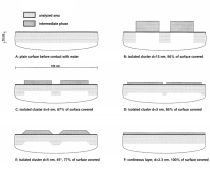
Silicate coatings for concrete components with waterglass systems by means of neutral salt initiation
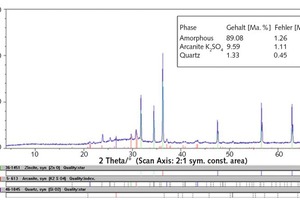
The objective of the investigations was the proof of the use of the neutral salt initiation as a construction material in the protecting silicate coating of concrete components, e.g. industry floors, factory finished parts or reinforced concrete construction parts, by means of waterglass fused silica suspensions.
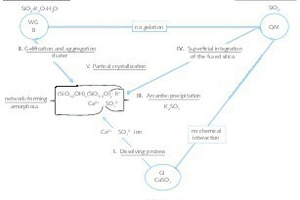
1 Colloid formation and sol-gel transition in
waterglass solutions
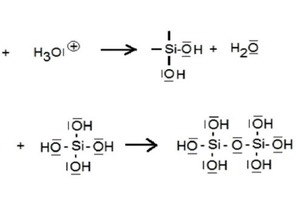
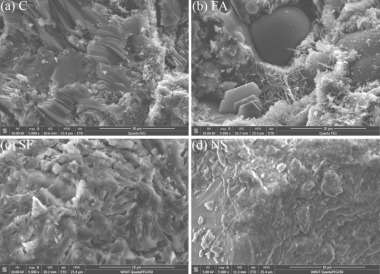
As early as around 1950, publications appeared describing and/or correlating the turbidity appearances and increasing viscosities of “aging” alkali waterglass solutions with the aid of the advanced light scattering measurement technology and establishing a relation to the formation of colloidal particles In “filtrated” sodium waterglass solutions with increasing waterglass module, particles with molecular weights of up to 10 000 (molar module 3.75) were found [1]. What is particularly remarkable is that a work by Brady and...