Synthesis of synthetic slag as a
replacement for industrial GGBS –
a boon for the cement industry
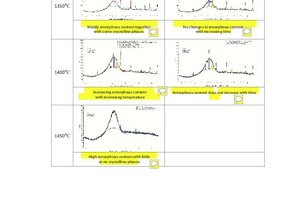
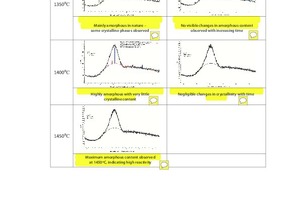
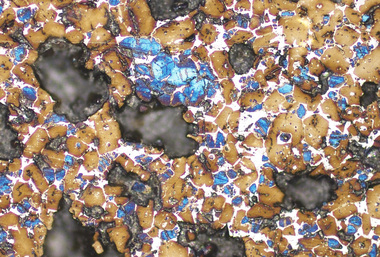
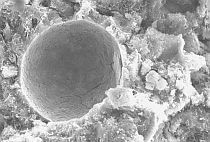
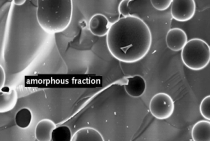
This study focuses on the effects of synthetic slag as an alternative to the existing, commercially available, GGBS slag in terms of the compressive strength of slag blended cement (SBC) pastes. Typically, these synthetic slags are prepared on a laboratory scale from limestone, pond ash, red mud and fly ash. Three types of slag were prepared from different raw mixes and the best slag was found with a maximum amorphous content at high temperature. This was examined further for the compressive strength of the slag blended cement. Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the percentage of amorphous content in each of the slags prepared. The results obtained indicate that synthetic slag can be considered as an alternative option to slag obtained from slag plants. This paper presents the results and conclusions of the laboratory trials with respect to the implementation of synthetic slag in SBC.
1 Introduction
Steel slag is produced [1] during the conversion of hot metal to crude steel during the melting of scrap in an electric arc furnace (EAF) or a basic oxygen furnace (BOF). Slag is basically used as a replacement for clinker in the cement industry because of its cementitious property [2].
In the steelmaking process slag is generated at a rate of approximately 100-200 kg/t of product in integrated plants using basic oxygen furnaces and 50 kg/t in electric arc furnace plants (mini-mills). Slag consists mainly of burnt lime and calcium silicates so it is possible that, with some...