Chloride penetration resistance of micron-nano materials modified mortar used as a concrete coating
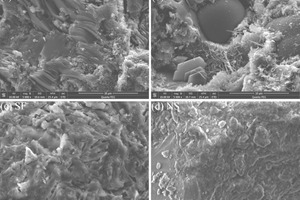
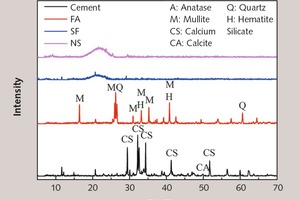
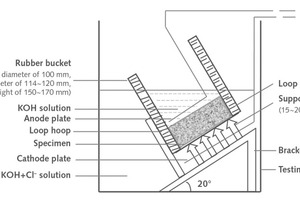
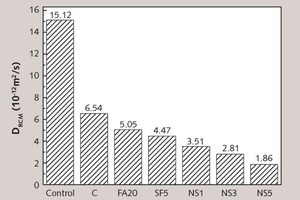
This study is intended to assess the ability to counter chloride diffusion of concrete applied with inorganic coating modified with different additives including fly ash (FA), silica fume (SF) and nano-SiO2 (NS). Experimental results reveal that the resistance against penetration of chloride is improved in the concrete specimens coated with special mortar coating compared to the non-coated specimen. Especially, concretes with NS modified mortar coating exhibit the most remarkable performance. Then the influence mechanisms of mortar coating mixed with different additives on the anti-chloride ion permeability of concrete are investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP). The results of the analyses indicate that the micro-aggregate filling effect of FA increased the density of the mortars, and thus reduced the chloride diffusion coefficient of the concrete. Three effects of SF and NS, including the heterogeneous nucleus effect, the high pozzolanic activity and the micro-aggregate filling effect, together increased the resistance to the chloride ion permeability of cement-based materials.
1 Introduction
In the field of construction, the 21st century is considered to be the century of the ocean [1]. In recent decades, with the steady development of the marine economy, the construction scale of ocean engineering became larger, the fields expanded, and scores of seaport buildings, coastal power plants, embankments, marine bridges and tunnels, land terminal and treatment facilities for offshore oil and gas fields as well as installation of subsea wires, pipelines and equipment are still being built. According to the State Oceanic Administration, the building industry of marine...